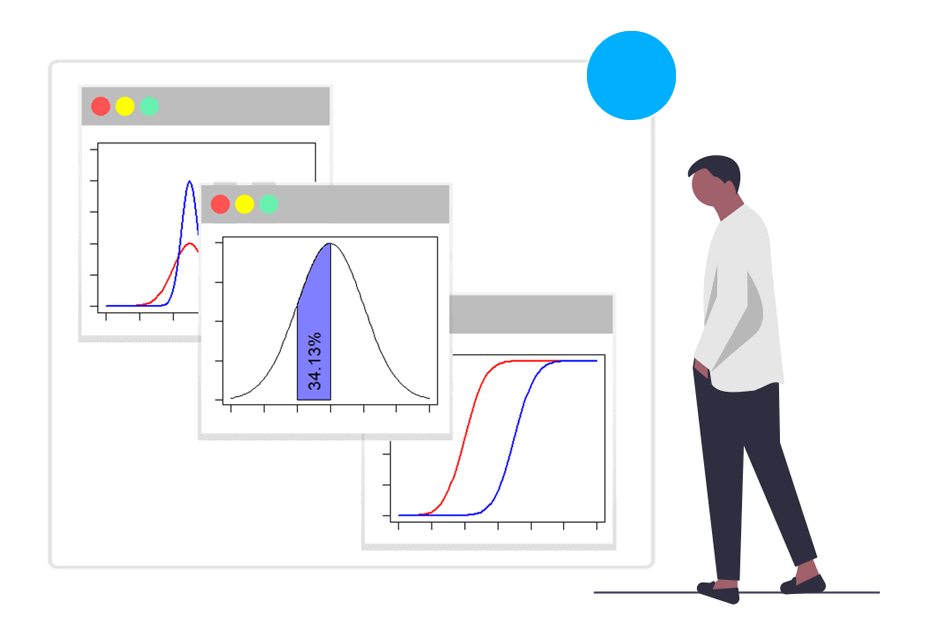
A statistical distribution, also known as a probability distribution, is a mathematical function that describes the likelihood of different outcomes or values occurring in a dataset or a random phenomenon
Continuous distributions describe the probability distribution of a continuous random variable. This type of random variable can take on any value within a specified range or interval, and the probability of obtaining any specific value is zero

dnorm() pnorm() qnorm() rnorm()
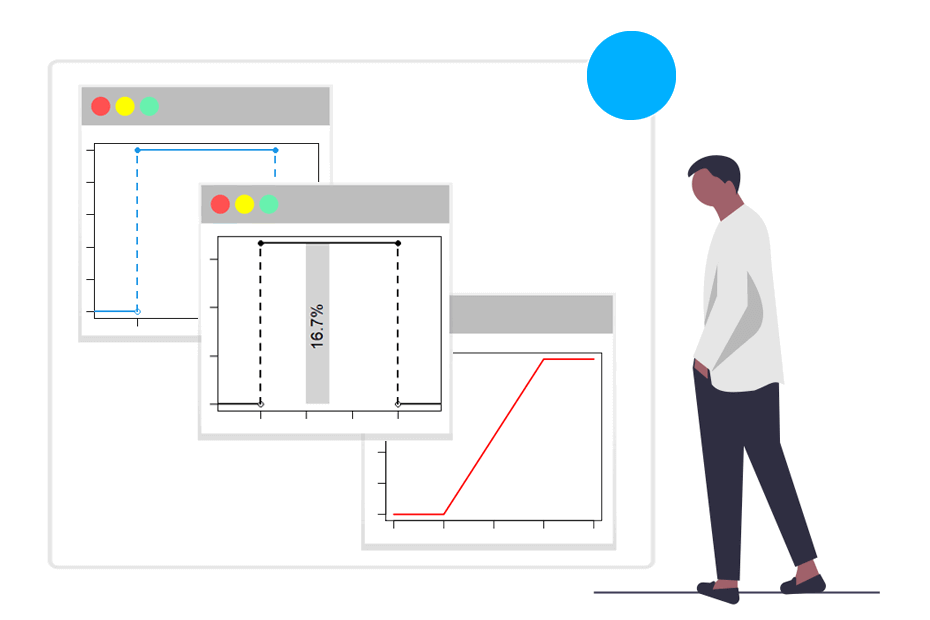
dunif() punif() qunif() runif()
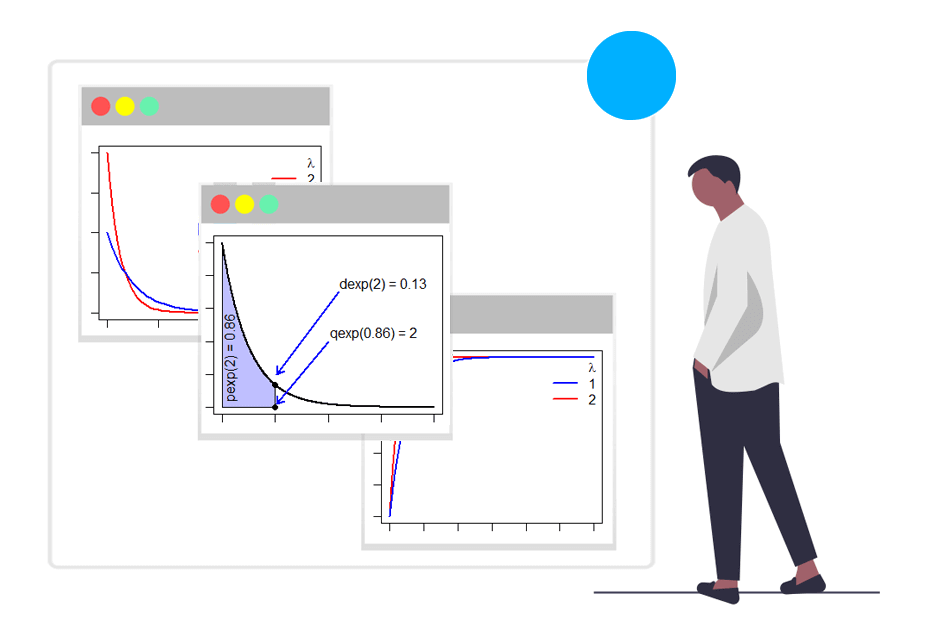
dexp() pexp() qexp() rexp()
Discrete distributions describe the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. This type of random variable can take on only distinct, separate values, typically integers, and the probability associated with each value is defined individually
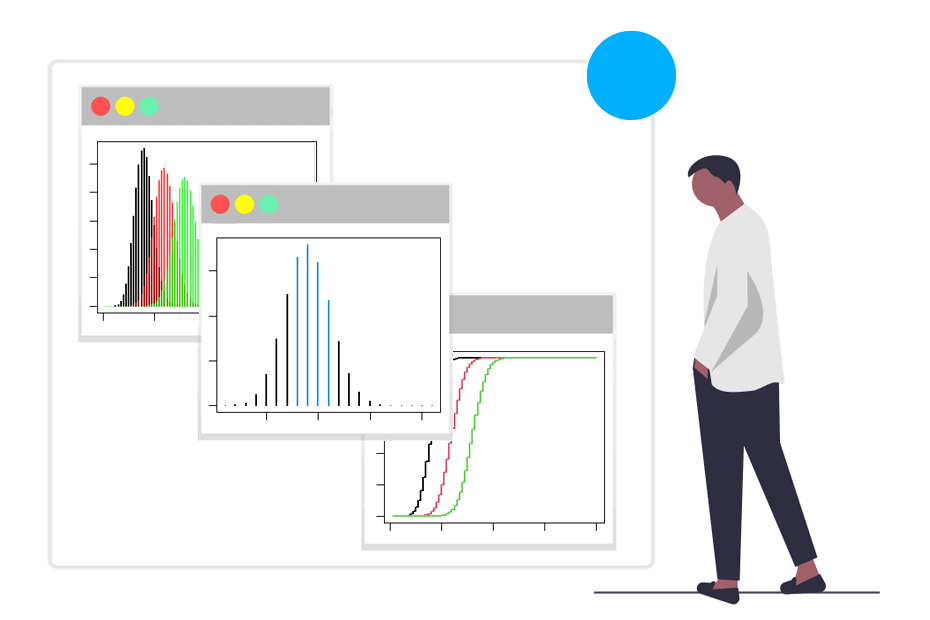
dbinom() pbinom() qbinom() rbinom()
dpois() ppois() qpois() rpois()
Copyright © 2024 - R CODER · All rights reserved Search for a tutorial Search also on R CHARTS Activate function search No results foundTry adjusting your search query
👉 If you haven’t found what you’re looking for, consider clicking the checkbox to activate the extended search on R CHARTS for additional graphs tutorials, try searching a synonym of your query if possible (e.g., ‘bar plot’ -> ‘bar chart’), search for a more generic query or if you are searching for a specific function activate the functions search or use the functions search bar.