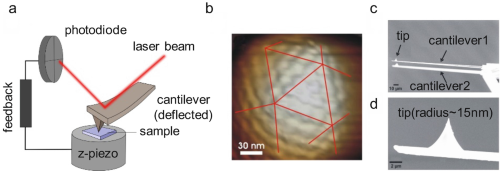
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1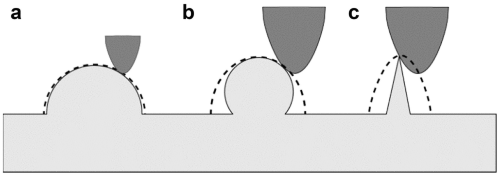 Fig. 2
Fig. 2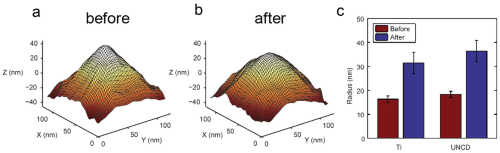 Fig. 3
Fig. 3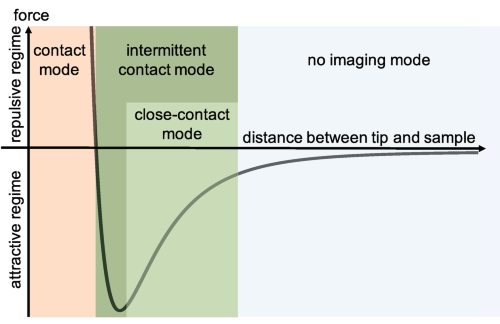 distance curve to illustrate the interaction between the cantileverCantilevers tipTip (probe) and the sample surface labeling the different operation modes" />Fig. 4
distance curve to illustrate the interaction between the cantileverCantilevers tipTip (probe) and the sample surface labeling the different operation modes" />Fig. 4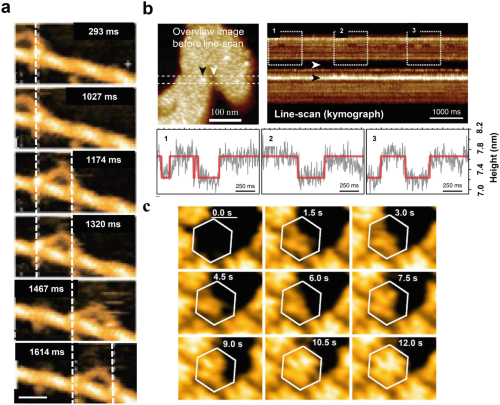 Fig. 5
Fig. 5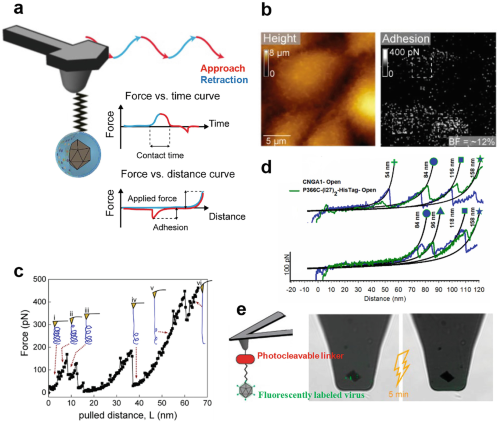 Fig. 6
Fig. 6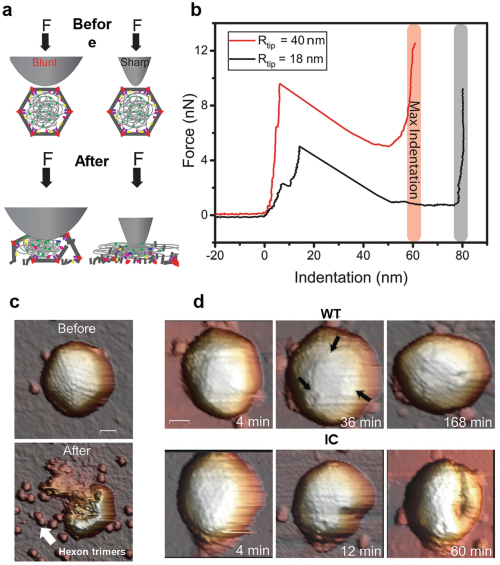 Fig. 7
Fig. 7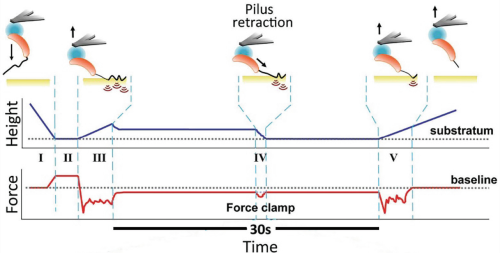 Fig. 8
Fig. 8Imaging of nano-sized particles and sample features is crucial in a variety of research fields, for instance, in biological sciences, where it is paramount to investigate structures at the single particle level. Often, two-dimensional images are not
Imaging of nano-sized particles and sample features is crucial in a variety of research fields, for instance, in biological sciences, where it is paramount to investigate structures at the single particle level. Often, two-dimensional images are not sufficient, and further information such as topography and mechanical properties are required. Furthermore, to increase the biological relevance, it is desired to perform the imaging in close to physiological environments. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) meets these demands in an all-in-one instrument. It provides high-resolution images including surface height information leading to three-dimensional information on sample morphology. AFM can be operated both in air and in buffer solutions. Moreover, it has the capacity to determine protein and membrane material properties via the force spectroscopy mode. Here we discuss the principles of AFM operation and provide examples of how biomolecules can be studied. New developments in AFM are discussed, and by including approaches such as bimodal AFM and high-speed AFM (HS-AFM), we show how AFM can be used to study a variety of static and dynamic single biomolecules and biomolecular assemblies.
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
Fig. 2 Fig. 3
Fig. 3 distance curve to illustrate the interaction between the cantileverCantilevers tipTip (probe) and the sample surface labeling the different operation modes" />Fig. 4
distance curve to illustrate the interaction between the cantileverCantilevers tipTip (probe) and the sample surface labeling the different operation modes" />Fig. 4 Fig. 5
Fig. 5 Fig. 6
Fig. 6 Fig. 7
Fig. 7 Fig. 8
Fig. 8